Office of Institutional Effectiveness Assessment
Assessment
"Measuring Student Learning and Success!"
Institutional Mission and Assessing Student Learning Outcomes
Emporia State University's mission is to prepare students for lifelong learning, rewarding careers, and adaptive leadership. The 2015-2025 strategic plan The Adaptive University includes five goals 1) Pursue distinctive initiatives in curricula and programs; 2) Develop the university’s capacity for adaptive leadership consistent with the Kansas Leadership Center framework; 3) Enhance the competitive role of Kansas by enrolling, retaining, and graduating students ready for life and career; 4) Create and support sustainable innovation and growth; and 5) Become a model for diversity, equity, and inclusion. The university is a complex organization with many operational units contributing, directly and indirectly, to ensure that students meet their higher education learning goals. Measuring the effectiveness of fulfilling these goals by assessing the quality of student learning experiences provides the decision-making data necessary to achieving success and continuously improving student learning.
Assessing student learning with the goal of continuously improving the quality of their learning experiences is essential to an institution-wide culture of adaptive change. These learning experiences occur systematically in a multi-contextual learning environment (classroom, online, co-curricular, extra-curricular, hybrid, and experiential). Intentionally adapting students' learning experiences is necessary to adequately prepare them for success in an innovative and dynamic 21st century. This requires strategic decision-making informed by quality assessment of student learning effectiveness. The Office of Institutional Effectiveness uses the National Institute for Learning Outcomes Assessment (NILOA) Transparency Framework as its guide for evaluating the extent to which Emporia State University makes evidence of student learning readily accessible, useful, and meaningful to various audiences.
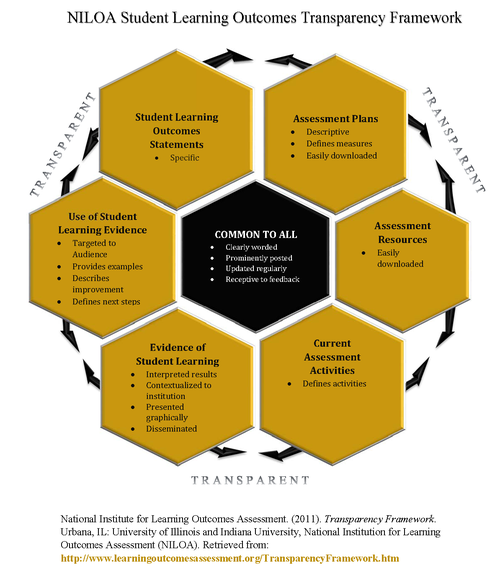
Student Learning Outcomes (SLO) Statements exist for all learning environments.
Academic degree programs have defined student learning outcomes as shown on the Student Learning Outcomes webpage, on the degree specific websites, and in various publications. The curriculum map lists program level student learning outcomes and the required courses that contribute to students' competently learning the content knowledge, skills, competencies, and practices specific to the degree program. Course level student learning outcomes are listed on every syllabus. An example shows the Mathematics program curriculum map and course syllabus. The syllabus serves to inform students of the course expectations and identifies how each course serves to educate the student towards having the knowledge, skills, and values required for their degree program of study. Each academic unit uses this mapping structure to ensure that students are prepared in their degree programs and to ensure academic programs are current. Faculty members are available to visit about program-specific student learning outcomes, and students are encouraged to proactively engage in their knowledge and understanding of how the curriculum is designed and improved upon.
Learning Themes and Outcomes are integrated into all co-curricular programming and consistent with academic programs are aligned with institution-wide learning goals. Co-curricular learning experiences are powerful and often provide students with the ability to hone and practice knowledge learned within the classroom. Keen on integrating learning experiences to engage students in making those connections between the world in which they live and how they can provide leadership for the common good is a by-product of co-curricular and academic programming. The Enrollment Management and Student Success division assesses the effectiveness of these student learning experiences and collaborates with academic leaders to make these learning experiences seamless.
The General Education Program learning goals are mapped to those courses contributing to student learning of foundations, core, transition, and transformation skills. The General Education Program assessment plan is grounded in analyzing student successes through multiple lenses. Using both direct and indirect data gathering provides a measurement of actual learning, meanwhile gaining an understanding of students perspectives on their educational experiences.
Assessment Plans are integrated throughout University Operations
The Adaptive University strategic plan consists of five goals with twenty-five supporting objectives, and represents a ten-year timeline ranging from July 1, 2015, through June 30, 2025. In 2017, the Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Plan was integrated into the strategic plan. In 2019, the plan was revised to ensure relevancy and currency. The plan also incorporates the Kansas Board of Regents Building a Future strategic plan and the ESU Campus Master Plan. Plan accountability is structured through the four functional tiers of the institution (Academic Affairs, Infrastructure, Enrollment Management & Student Success, and Administration and Finance). In addition, the ESU Foundation serves a vital role in supporting the institution in fulfilling its mission and strategic plan as philanthropic efforts provide crucial financial support. The Assessment Plans web page provides a detailed description with supporting documentation of the institution-wide assessment planning operations.
Assessment Resources are vital to building capacity and ensuring that the campus community is informed.
The Office of Institutional Effectiveness (OIE) shares and distributes assessment information across the institution through the operations of the Student Learning Assessment Council (meeting documents). All information is available on the website on the Assessment Resources web page. The council shares information with their faculty and staff. It is common for workshops and council meetings to serve as assessment knowledge shares and provide individual and group assessment training opportunities.
- Workshop topics are identified through consultation with the faculty at the discipline and program levels.
- Some academic programs seek direct assistance with faculty development opportunities, meanwhile most workshops are attended by individuals representing a variety of disciplines.
- Individual faculty members are encouraged to engage in individual consultations and professional development opportunities.
- The faculty is supported in attending assessment workshops and conferences at other venues and institutions.
- A canvas online course dedicated to professional development in assessment is available to all ESU faculty and staff free of charge.
- A variety of assessment literature and books are available for checkout through the OIE as well as the WAW Libraries and Archives. Common titles available are Assessing General Education Programs (Allen, M.J., 2006), Assessing Academic Programs in Higher Education (Allen, M.J., 2004), Assessing and Improving Student Organizations (Nolfi, T. and Ruben, B.D., 2010), Assessment in Practice (Banta, T.W., Lund, J.P., Black, K.E., and Oblander, F.W., 1996, Assessment Essentials (Banta, T.W. and Palomba, C.A., 2015), Assessment Clear and Simple (Walvoord, B.E., 2010), Assessment Reconsidered (Keeling, R.P., Wall, A.F., Underhile, R., and Dungy G.J., 2008), Assessing Student Learning (Suskie, L., 2009), Classroom Assessment Techniques (Angelo, T.A. and Cross, K.P., 1993), Assessment Reconsidered 2 (Keeling R.P., Editor, 2006), Assessment in Student Affairs: A Guide for Practitioners (Upcraft, L.M, and Schuh, J.H., 1996), and Designing & Assessing Courses & Curricula (Diamond, R.M., 1998) to list a few.
Current Assessment Activities and the Assessment of Student Learning
The campus community engages in assessment activities on a continuous basis and at all operational levels. The assessment of the institution's effectiveness in meeting its mission is confirmed through the strategies aligned with objectives identified in the strategic plan, all of which are aligned with student learning and success.
- Assessment reporting generally occurs at the end of each of the fall and spring terms or annually at the end of June.
- Course-embedded assessments are dedicated to improving learning at the formative levels and collectively contribute to improving both program and general education curricula.
- The faculty is engaged in these assessment activities for assigned courses.
- Unit level assessments are directed toward coordinating the faculty in ways which inform the disciplines.
- In assessing general education, the focus is at the course and goal levels. At the goal level, courses contributing (i.e., critical thinking skills) are identified across the disciplines and the interdisciplinary contributions are measured using a common rubric. These assessments are currently focused on the core skills, analytical reasoning, creative thinking, cultural awareness & cultural competence, integrated learning, breadth of knowledge, and critical thinking. Together these multiple level assessment activities inform the improvement of student learning at many different levels concurrently.
Using Student Learning Evidence
Evidence of student learning is captured and shared transparently across the institution and in many situations presented transparently on the Emporia State University and Kansas Board of Regents websites.
- The evidence represents both internal and external data gathering techniques and is contextualized in a variety of written and graphical formats depending on the instruments and assessments being used to measure student learning.
- The audience receiving the information is taken into consideration and often there are many levels of data share depending on how the information can best be used to inform student learning improvement efforts. For example, the Senior Survey results are shared campus-wide allowing for the various entities to review the information and develop strategies for improving the student learning experience.
Assessment Informing Change Strategies
There are multiple ways that assessment informs change to improve the student learning experience. Oftentimes, strategies that impact learning effectiveness are employed on a day-to-day basis by faculty as they instruct courses. These adjustments are made as faculty analyze and implement changes throughout the semester based on formative assessments of student learning as it is occurring. These improvements in the learning experiences are driven by individual faculty members who are expert in the craft of teaching. Faculty articulation and reflection on these improvement strategies are collected through course assessment reports at the end of a term. By far, this is the most frequently employed practice in improving student learning experiences.
The Annual Assessment Report is multi-year accumulation of academic assessment efforts and is produced and distributed annually. This document serves to inform stakeholders of the assessment efforts that occur on an annual basis and also serves as an evidence repository for affiliated documentation of assessment efforts.
